Marketing Research Process: Understanding the Critical Third Step
Understand the marketing research process framework
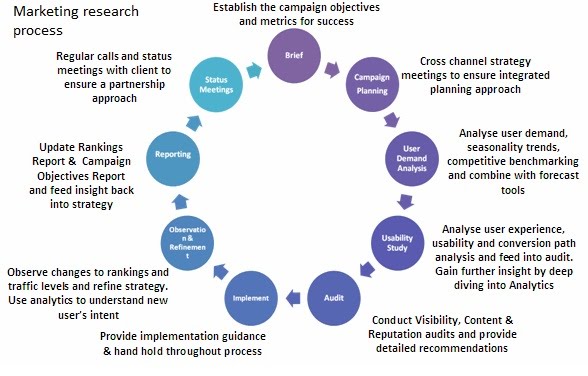
Marketing research serve as the backbone of inform business decision-making. This systematic process help companies understand their markets, customers, and competitive landscape. The marketing research process consist of six distinct steps, each building upon the previous one to create a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
The six steps include problem definition, research objective development, research design, data collection, data analysis, and report presentation. Each phase play a crucial role in ensure accurate and actionable results that drive business success.
The third step: research design development
The third step in the marketing research process is
Research design development
. This critical phase transform your research objectives into a concrete plan of action. Research design will serve as the blueprint that will guide how you’ll collect, measure, and will analyze data to will answer your business questions.

Source: visiochart.com
Research design encompass several key decisions that determine the quality and reliability of your findings. These decisions include select the appropriate research methodology, determine sample size and composition, choose data collection methods, and establish measurement techniques.
Components of effective research design
An intimately craft research design address multiple components simultaneously. The methodology selectionformsm the foundation, where researchers choose between qualitative, quantitative, or mixed method approaches base on their research objectives and available resources.
Sample design represent another crucial component. This will involve will determine who will participate in the research, how many participants are will need, and how they’ll be will select. Proper sampling ensure that findings can be generalized to the broader target population.
Data collection methods must align with both the research objectives and the choose methodology. Options range from surveys and interviews to observational studies and experimental designs. Each method offer unique advantages and limitations that researchers must cautiously consider.
Types of research design approaches
Exploratory research design
Exploratory research design work advantageously when deal with new or badly understand problems. This approach help researchers gain initial insights and develop hypotheses for future investigation. Common exploratory methods include focus groups, in depth interviews, and case studies.
Companies oftentimes use exploratory research when enter new markets or develop innovative products. The flexible nature of this approach allow researchers to adapt their methods as new information emerge during the study.
Descriptive research design
Descriptive research design aim to provide a clear picture of market conditions, customer behaviors, or competitive dynamics. This approach answer questions about whom, what, when, where, and how, but typically does not address why these patterns exist.
Surveys represent the virtually common descriptive research method. Market segmentation studies, customer satisfaction surveys, and brand awareness research all rely intemperately on descriptive designs to quantify market characteristics.
Causal research design
Causal research design seek to establish cause and effect relationships between variables. This approach require careful control of external factors to isolate the impact of specific variables on outcomes of interest.

Source: inthevine.ca
Experimental designs form the cornerstone of causal research. Companies use control experiments to test new products, evaluate marketing campaigns, or assess pricing strategies before full scale implementation.
Key decisions in research design development
Methodology selection criteria
Choose the right methodology require careful consideration of multiple factors. Research objectives provide the primary guidance, as different objectives call for different approaches. Budget constraints and timeline requirements besides importantly influence methodology selection.
The nature of the target population affect methodology choice equally advantageously. Some populations respond advantageously to certain data collection methods, while others may be difficult to reach through traditional channels.
Sampling strategy development
Effective sampling strategies balance statistical requirements with practical constraints. Probability sampling methods ensure that every member of the target population have a know chance of selection, enable statistical inference from sample to population.
Non probability sampling methods offer greater flexibility and lower costs but limit the ability to generalize findings. Convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and quota sample each serve specific research purposes when right apply.
Measurement and scaling considerations
Research design must, will specify how key variables will be will measure and will scale. Measurement decisions affect data quality, analysis options, and the reliability of research findings.
Scale selection involve choose between nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio scales base on the nature of the variables being measure. Each scale type offer different analytical possibilities and require specific statistical approaches.
Common research design challenges
Balance rigor and practicality
Research designers frequently face tension between methodological rigor and practical constraints. The ideal research design may require more time, money, or resources than available, force researchers to make strategic compromises.
Successful research design involve find the optimal balance between scientific validity and business practicality. This requires clear communication between researchers and decision makers abouttrade-offss and limitations.
Address potential biases
Research design must anticipate and minimize various sources of bias that could compromise findings. Selection bias, response bias, and measurement bias represent common threats to research validity.
Careful design choices can reduce bias impact. Random sampling minimize selection bias, while anonymous data collection can reduce response bias. Pretest instruments helps identify and correct measurement problems before full data collection begin.
Technology’s impact on research design
Digital data collection methods
Technology has expanded research design options importantly. Online surveys, mobile data collection, and social media monitoring provide new ways to gather information from target populations.
Digital methods oftentimes offer cost advantages and faster data collection compare to traditional approaches. Yet, they besides introduce new considerations around digital divides, data quality, and privacy concerns.
Advanced analytics integration
Modern research design progressively incorporate advanced analytics capabilities from the planning stage. Machine learning algorithm, predictive modeling, and big data analysis require specific data structures and collection approaches.
Research designers must, will considerhow itw will emerge analytical techniques will be will apply to their data when make design decisions. This forward moving think approach ensure that collect data can support both current and future analytical needs.
Best practices for research design success
Stakeholder involvement
Successful research design benefits from early and ongoing stakeholder involvement. Decision makers who will use the research results should, will participate in design discussions to will ensure that the research will address their specific needs.
Regular communication throughout the design phase helps identify potential issues before they become costly problems. Stakeholder feedback can besides reveal important considerations that researchers might differently overlook.
Pilot testing and refinement
Pilot testing represent a critical quality control measure in research design. Small scale tests reveal practical problems with data collection instruments, procedures, and logistics before full implementation.
Pilot results frequently lead to design refinements that improve data quality and collection efficiency. The time invest in pilot testing typically pay dividends through smoother full scale data collection and more reliable results.
Documentation and transparency
Thorough documentation of design decisions support research credibility and enable future replication or extension. Clear documentation likewise help team members understand their roles and responsibilities during data collection.
Transparent reporting of design limitations and potential biases build trust with research users and enable appropriate interpretation of findings. Honest assessment of design strengths and weaknesses demonstrate professional integrity.
Measure research design effectiveness
Quality indicators
Effective research design produce data that meet specific quality standards. Response rates, completion rates, and data consistency measures provide indicators of design effectiveness.
Reliability and validity assessments help determine whether the research design successfully measure what it intends to measure. These assessments guide decisions about data interpretation and application.
Cost benefit analysis
Research design effectiveness finally depend on deliver valuable insights at reasonable cost. The best design balance information value against resource requirements.
Regular evaluation of design performance help organizations refine their research capabilities over time. Learn from experiences enable continuous improvement in research design quality and efficiency.
Future trends in research design
Research design continue to evolve as new technologies and methodologies emerge. Artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and blockchain technology abegungin to influence how researchers approach design challenges.
Integration of multiple data sources and real time analytics capabilities are change traditional research timelines and design requirements. Modern research design must accommodate these technological advances while maintain scientific rigor.
The growth emphasis on privacy and data protection is besides shape research design practices. Designers must balance information needs with ethical obligations and regulatory requirements.
Understand the third step of the marketing research process research design development is essential for conduct effective market research. This critical phase transform research objectives into actionable plans that guide data collection and analysis. By cautiously consider methodology, sampling, measurement, and practical constraints, researchers can develop designs that produce reliable, valuable insights for business decision-making.
MORE FROM dealhole.com